Fine Chemical
- Home
- Investment Opportunities
- Industries
- Fine Chemical
-
Attractiveness of the Korean Chemical Industry With Solid Demands from High-tech Downstream Industries CloseAttractiveness of the Korean Chemical Industry With Solid Demands from High-tech Downstream IndustriesThe overall global chemical industry has matured and is growing slowly at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 2%. As a result, chemical companies around the world are rushing to develop high-value-added products to maintain stable profitability. The reorganization of the global supply chain triggered them to continue investing in countries with high-tech downstream industries. Considering that Korea has major high-tech industries such as semiconductor and display, electric and electronics, automotive, secondary battery, and hydrogen, the country's anchor companies leading global trends are important customers for global chemical companies that supply various core materials required for producing finished products. In particular, with the global supply chain shifting the focus from efficiency to stability, several global chemical and materials companies have expressed their willingness to operate production bases and R&D centers near the factories of Korean anchor companies."Korea’s Major High-tech Downstream Industries and Anchor Companies"
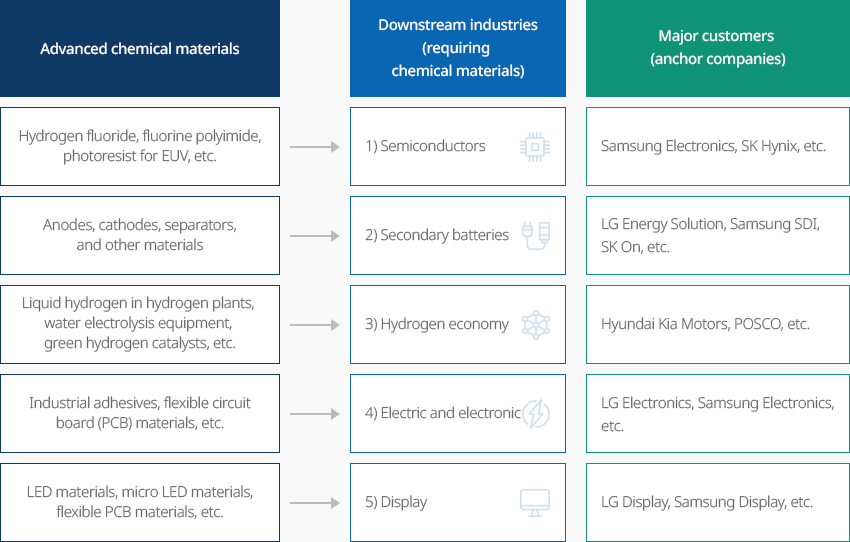 Advanced chemical materials
Advanced chemical materials- Hydrogen fluoride, fluorine polyimide, photoresist for EUV, etc.
- Anodes, cathodes, separators, and other materials
- Liquid hydrogen in hydrogen plants, water electrolysis equipment, green hydrogen catalysts, etc.
- Industrial adhesives, flexible circuit board (PCB) materials, etc.
- OLED materials, micro LED materials, flexible PCB materials, etc.
Downstream industries (requiring chemical materials)- 1) Semiconductors
- 2) Secondary batteries
- 3) Hydrogen economy
- 4) Electric and electronic
- 5) Display
Major customers (anchor companies)- Samsung Electronics, SK Hynix, etc.
- LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, SK On, etc.
- Hyundai Kia Motors, POSCO, etc.
- LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics, etc.
- LG Display, Samsung Display, etc.
 ※ Source : KOTRA Invest KOREA
※ Source : KOTRA Invest KOREA -
Korea, World's 5th Largest Chemical Powerhouse OpenKorea, World's 5th Largest Chemical PowerhouseKorea's chemical industry is a giant industry, ranking fifth globally with sales reaching USD 115 billion and accounting for about 3.0% of the global market. The production capacity of ethylene, a basic petrochemical material, is used as a measure of a country's chemical industry, and Korea is the world's fourth biggest producer, producing 12.7 million tons (about 6.2%) of the world's total ethylene production of 250 million tons in 2021.Backed by the upstream industry ensuring a stable and sufficient supply of high-quality raw materials, Korea's fine chemical industry produces core and applied materials for various downstream industries (e.g., semiconductors, displays, automobiles, secondary batteries, and hydrogen) based on an industrial structure that is capital, knowledge, and technology-intensive.The American Chemical Society (ACS) ranked the world's top 50 global chemical companies based on sales in 2021, and Korea boasted its world-class chemical industry with three Korean companies (Lotte Chemical, Hanwha Solutions and GS Caltex) on the list, as well as LG Chem at ninth place.
 "Ethylene Production Capacity in 2021" (Unit: million tons/year)
"Ethylene Production Capacity in 2021" (Unit: million tons/year)- World : 205.5
- US : 19.7
- China : 19.4
- Saudi Arabia : 8.6
- Korea : 6.2
- Iran : 3.8
- India : 3.6
※ Source: Korea Petrochemical Industry Association"Top 50 Chemical Companies in 2021"- 1 : BASF (Germany)
- 2 : Sinopec (China)
- 3 : DOW (US)
- 9 : LG Chem
- 10 : ExxonMobil (US)
- 28 : Lotte Chemical
- 39 : Hanwha Solutions
※ Source: American Chemical Society (ACS) Chemical products are Korea’s third most exported item following semiconductors and automobiles. Korea's chemical product exports stood at USD 1.3 billion in the 1990s when the products were globally competitive. Since then, the amount has increased more than 40-fold to USD 55.1 billion in 2021."Korea's Top 5 Export Products: Export Value and Trade Balance in 2021"(Unit: USD 100 million)
Chemical products are Korea’s third most exported item following semiconductors and automobiles. Korea's chemical product exports stood at USD 1.3 billion in the 1990s when the products were globally competitive. Since then, the amount has increased more than 40-fold to USD 55.1 billion in 2021."Korea's Top 5 Export Products: Export Value and Trade Balance in 2021"(Unit: USD 100 million)Korea's Top 5 Export Products: Export Value and Trade Balance in 2021 Category, Semiconductors, Automobiles, Petrochemical, General machinery Steel Category Semiconductors Automobiles Petrochemical General machinery Steel Export value 1,280 692 551 530 364 Trade balance +666 +488 +404 +214 +119 ※ Source: Korea International Trade AssociationIn 2022, foreign direct investment (FDI) in the chemical materials sector amounted to approximately USD 7.9 billion, not only recovering the pre-COVID-19 pandemic level, but also reaching the highest level in the last five years and increasing significantly by more than five times year-on-year. Despite the growing uncertainties in the global economy triggered by the war in Ukraine and interest rate hikes, FDI in all three sub-sectors of the chemical materials sector (i.e., chemical engineering, metals and metal processing, and secondary battery manufacturing) grew evenly. In particular, more overseas companies specializing in materials, parts and equipment are investing in Korea to tap into the nation's supply chains of high-tech industries, such as semiconductors, electronics, automobiles, and secondary batteries, and are expected to contribute to the establishment of a stable value chain with companies requiring the high-tech products and facilitate exports."FDI in the Chemical Materials Industry (2018-2022)"(Unit: USD million, cases)FDI in the Chemical Materials Industry (2018-2022) Category, Year Category 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Cases Amount Cases Amount Cases Amount Cases Amount Cases Amount Chemical engineering 126 1,822 87 3,944 69 991 83 921 72 5,366 Metals and metal processing 43 355 35 24 26 64 42 113 37 565 Primary battery and battery manufacturing (including secondary batteries) 9 256 5 30 6 286 10 535 10 1,960 Total 178 2,433 127 3,998 96 1,341 116 1,570 119 7,891 ※ Source: KOTRA FDI Statistics (INSC)Centered on the three major chemical clusters of Ulsan, Yeosu (Jeonnam), and Daesan (Chungnam), the Korean chemical industry has achieved the economies of scale necessary for developing the large-scale device industry. The industry also has achived a high degree of vertical integration from crude oil to high-tech materials and excellent production management capabilities, facilitating Korean chemical companies' expansion into newly emerging high-tech industries such as secondary batteries and hydrogen. However, the product portfolios of many Korean chemical companies are still composed of general-purpose products and sales are mostly focused on Korea and China. The nation's the level of technology is relatively inferior to those of major players such as the United States and Europe, but Korean companies are rapidly developing and securing original technologies for key materials, components, and equipment, while expanding their partnerships in forms such as joint ventures with foreign companies interested in investing in the Korean chemical industry."Korean Chemical Industry: SWOT Analysis"
-
Strength - Internal environment
- Economies of scale enabled by the three major chemical industrial complexes
- High level of vertical integration (crude oil → high-tech materials)
- (Secondary battery) Leading companies in EVs and secondary batteries
- (Hydrogen) Systematic nurturing of the hydrogen industry based on Korea's leadership in hydrogen vehicles and the passage of the Hydrogen Act
-
Weakness - Internal environment
- High proportion of general-purpose products
- siness structure concentrated in Korea and China
- (Secondary battery) High reliance on imported core materials
- (Hydrogen) Limited value chain of materials, parts, and equipment for green hydrogen production compared to other leading countries
-
Opportunity - External environment
- Growth of specialty chemical and eco-friendly chemical material markets
- Increased demand for chemical products from emerging Asian countries (FTA)
- Active JVs and M&As among chemical companies
- (Secondary battery) Growth momentum of the EV market (annual 30%)
- (Hydrogen) Growth of hydrogen vehicle market (annual 32%), countries strengthening efforts to foster the hydrogen industry and the Middle East driving hydrogen businesses
-
Threat - External environment
- Global economic downturn and oversupply in the chemical industry
- (Emerging countries) China and the Middle East increasing the self-sufficiency of chemical products
- (Developed countries) Reorganizing the business structure centered on high added-value
- (Secondary battery) Intensified weaponization of core material resources
- (Hydrogen) Technologies dominated by hydrogen leaders such as the US and EU, and China's offensive with low-cost green hydrogen
 ※ Source : KOTRA Invest KOREA
※ Source : KOTRA Invest KOREA -
Latest Chemical Industry Investment Success Stories OpenLatest Chemical Industry Investment Success StoriesT (Japanese company) to expand high-performance engineering plastics plantIncreasingly being used in high-tech industries such as eco-friendly vehicles, secondary batteries, and electrical and electronic devices, engineering plastics are at the center of a fierce global competition aimed at securing technology. Company T leading the global advanced materials market has expanded its manufacturing base in Korea, raising expectations that it will contribute to the formation of a stable value chain with Korean businesses needing engineering plastics and to the development of related technologies. Southeast Asia with its relatively-low investment costs competed with Korea to attract Company T's investment, but the company decided to invest in Korea after the Korean government offered various incentives in Korea and Japan.S (Saudi company) to build a new multi-purpose petrochemical plant in UlsanDespite global economic uncertainties, Company S announced plans to invest KRW 9 trillion from 2023 to 2026 to produce chemicals such as ethylene and propylene and high-value-added plastics in Ulsan. According to the Ulsan city government, the massive investment is expected to create up to 17,000 jobs during the construction period and revitalize the local construction industry valued at more than KRW 3 trillion. The company plans to commercialize for the first time in the world a TC2C (Thermal Crude to Chemicals) facility, which converts low-value heavy oil products from existing refineries into raw materials used in steam crackers that produce petrochemical raw materials.

-
Government Policies Supporting the Chemical Industry OpenGovernment Policies Supporting the Chemical IndustryIn October 22, the Korean government announced the Materials, Parts and Equipment Industry Policy Direction of the New Government and upgraded the goals from facilitating localization and self-reliance to dominating the global market. Accordingly, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) has its Materials, Parts, and Equipment Globalization Strategy passed in a Cabinet meeting in April 23. The government plans to focus on supporting related areas by expanding the scale of 150 key strategic technologies of the materials, parts and equipment industry in seven major fields* to 200 technologies in 10 fields, which includes space, defense and hydrogen. Fifteen technologies related to eco-friendly and low-carbon materials are included in the list. In addition, ministries are jointly working to ease regulations, with the Ministry of Environment seeking to shorten the risk and suitability notification period for installing and operating facilities handling hazardous chemicals.* (Existing seven areas) Semiconductor, display, automotive, machinery and metal, electric and electronic, basic chemical, bio, (Newly added areas) Space, defense, and hydrogen."Chemical Industries Included in Key Strategic Technologies of the Materials, Parts and Equipment Industry (as of Oct. 2022)"
Chemical Industries Included in Key Strategic Technologies of the Materials, Parts and Equipment Industry (as of Oct. 2022) Category, No., Technologies 정보제공 Category No. Technologies Chemical 1 Fluorinated Materials Manufacturing Technology 2 Elastic Materials and Parts Manufacturing Technology 3 Adhesive Materials Manufacturing Technology 4 Epoxy Materials Manufacturing Technology 5 Paint and Coating Materials Manufacturing Technology 6 High Performance Engineering Plastics Materials Manufacturing Technology 7 Biodegradable Fiber Materials Manufacturing Technology 8 Chemical Process Catalyst Technology 9 Biodegradable Plastics Manufacturing Technology 10 Biomass-based fiber manufacturing technology 11 Cellulose-based Fiber Manufacturing Technology 12 Recycled fiber manufacturing technology 13 Spinning Oil Manufacturing Technology 14 Dispersible Dye and Ink Manufacturing Technology 15 Lightweight Durable Composites Manufacturing Technology "Investment Incentives"Investment Incentives Category, Description Category Description Cash subsidies - Up to 50% of foreign direct investment (FDI)
* Scope of support determined based on a comprehensive evaluation of technology level, job creation effect, and compatibility with domestic industries
Location support - Reduced rent (100%, up to 50 years) for sites designated as foreign investment zones
Tax benefits National Tax - General Tax Credit on Investment
- (General) 3%
- (New Growth and Original Technologies) 8%
- (National Strategic Technologies) 15%
- Tax Credit on R&D (deduction for researcher training)
- (General) 2%
- (New Growth and Original Technologies) Max. 30%
- (National Strategic Technologies) Max. 40%
- Tariff and Value-Added Tax Exemption
- Exemption from tariff and value-added taxes for 5 years for capital goods*
introduced in accordance with the Foreign Investment Promotion Act
* Machinery, equipment, parts, etc. used as industrial facilities (including ships, vehicles, airplanes, etc.)
- Exemption from tariff and value-added taxes for 5 years for capital goods*
introduced in accordance with the Foreign Investment Promotion Act
- (Companies operating in Saemangeum) Five-year reduction of corporate tax
- 100% for the first 3 years, 50% for the remaining 2 years
Local Tax - (For new growth engine companies and companies operating in special areas such
as foreign investment zones)
Reduction of acquisition tax and property tax for 7 years (100% for 5 years + 50%
for 2 years) on property acquired and owned by foreign-invested companies
* Reduction can be extended up to 15 years according to local government ordinances.
Income Tax - Foreign engineers * 50% reduction in income tax on earned income for 10
years
* (Definition) △ Technology providers under engineering technology introduction contracts, △ Researchers working in R&D facilities of foreign-invested companies
- Foreign workers * Income tax reduction for 20 years on earned income (19% single
tax rate on earned income*)
* (Definition) △ Foreign workers (excluding foreign executives and day laborers who are employers), △ Workers of regional headquarters recognized by the Foreign Investment Promotion Act
** Allowed to choose between the general income tax rate (6-45%) and the 19% single tax rate.
- Up to 50% of foreign direct investment (FDI)
-
Korea’s Three Major Chemical Industrial Complexes Enhancing Competitiveness of the Chemical Industry OpenKorea’s Three Major Chemical Industrial Complexes Enhancing Competitiveness of the Chemical IndustryCentered around the three major chemical industrial complexes in Ulsan, Yeosu (in Jeonnam), and Daesan (in Chungnam), the Korean chemical industry has achieved economies of scale essential for the development of the large-scale process industry. In particular, the complexes in Ulsan and Yeosu are the largest chemical industrial complexes in Asia and serve as engines for the development of Korea's chemical industry. In Ulsan, the world's leading chemical companies such as SK Energy, S-OIL, Eastman, BP, and Dupont are actively producing products, and the chemical industrial complex in Yeosu is home to global chemical companies such as GS Caltex, DL Chemical, Hanwha Solutions, Korea BASF, and Lotte Versalis. In the chemical industrial complex in Daesan, major Korean chemical companies such as Lotte Chemical, LG Chem, and Hyundai Oilbank are operating. A hydrogen industry ecosystem is also in place in the complex, with Lotte-Air Liquide Ener'Hy, a joint venture of Lotte Chemical and Air Liquide Korea, building a hydrogen by-product shipping center."Korea’s Three Major Chemical Industrial Complexes"
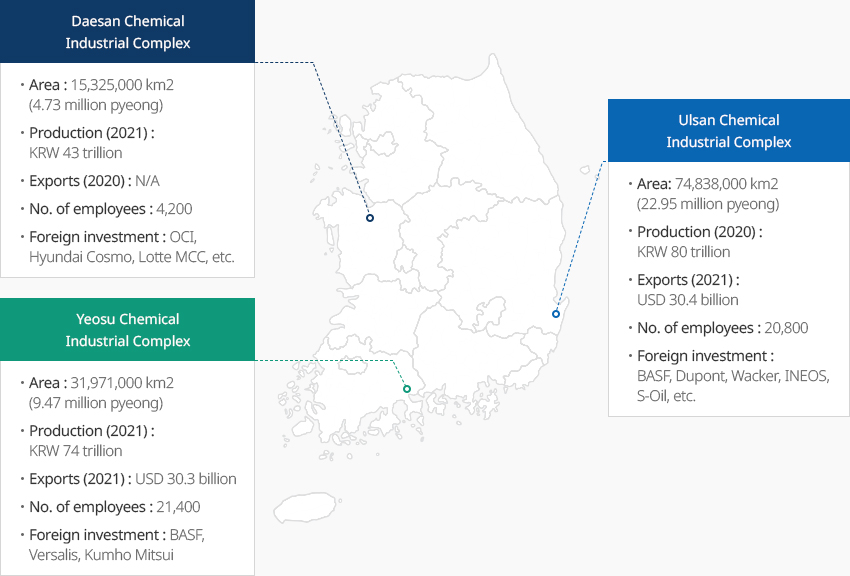
- Daesan Chemical Industrial Complex
- Area : 15,325,000 km2 (4.73 million pyeong)
- Production (2021) : KRW 43 trillion
- ports (2020) : N/A
- No. of employees : 4,200
- Foreign investment : OCI, Hyundai Cosmo, Lotte MCC, etc.
- Yeosu Chemical Industrial Complex
- Area : 31,971,000 km2 (9.47 million pyeong)
- Production (2021) : KRW 74 trillion
- Exports (2021) : USD 30.3 billion
- No. of employees : 21,400
- Foreign investment : BASF, Versalis, Kumho Mitsui
- Ulsan Chemical Industrial Complex
- Area : 74,838,000 km2 (22.95 million pyeong)
- Production(2020) : KRW 80 trillion
- Exports (2021) : USD 30.4 billion
- No. of employees : 20,800
- Foreign investment : BASF, Dupont, Wacker, INEOS, S-Oil, etc.
 ※ Source: Korea Petrochemical Industry Association
※ Source: Korea Petrochemical Industry Association - Daesan Chemical Industrial Complex
-
Complex nameManjeong General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2010.02.05
-
Designated area(m2)50,401
-
ManagementChungcheongbuk-do Chungju City
-
Nearby RailwayDalcheon Station
-
Distance from station(km)5
-
Nearby AirportCheongju International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)51
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)177(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentChungcheongbuk-do Chungju City
-
Population210,304
-
Complex nameUlsan Techno General Industrial Complex(Ulsan Free Economic Zone)
-
Initial designation date2013.06.20
-
Designated area(m2)1,286,977
-
ManagementUlsan Metropolitan City
-
Nearby RailwayTaehwagang Station
-
Distance from station(km)9
-
Nearby AirportUlsan Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)15
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)2614(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentUlsan Metropolitan City Nam-gu
-
Population1,140,310
-
Complex nameImphi Agricultural Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2011.06.20
-
Designated area(m2)239,156
-
ManagementJeollabuk-do Gunsan City
-
Nearby RailwayDaeya Station
-
Distance from station(km)7
-
Nearby AirportGunsan Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)31
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)426(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentJeollabuk-do Gunsan City
-
Population267,982
-
Complex nameYesan New Material General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2011.06.16
-
Designated area(m2)483,670
-
ManagementChungcheongnam-do Yesan County
-
Nearby RailwaySillyewon Station
-
Distance from station(km)22
-
Nearby AirportCheongju International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)87
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)788(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentChungcheongnam-do Yesan County
-
Population78,420
-
Complex nameBusan New Material General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2013.01.16
-
Designated area(m2)255,229
-
ManagementBusan Economic Promotion Agency
-
Nearby RailwayBusan Station
-
Distance from station(km)47
-
Nearby AirportGimhae International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)48
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)0.27(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentBusan Metropolitan City Gijang County
-
Population172,288
-
Complex nameCeramic General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2009.06.05
-
Designated area(m2)116,361
-
ManagementJeollanam-do Mokpo City
-
Nearby RailwayMokpo Station
-
Distance from station(km)5
-
Nearby AirportMuan International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)36
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)-
-
Affiliation local governmentJeollanam-do Mokpo City
-
Population226,875










