- Home
- Investment Opportunities
- Industries
- Aerospace
Aerospace
-
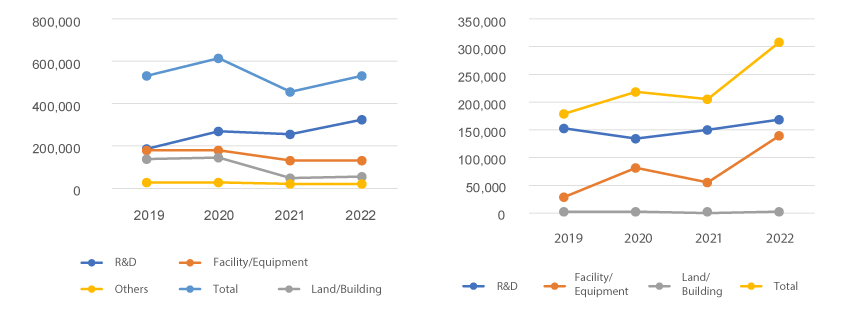
Consistent Investment in R&D for Technological Advancement 내용닫기Consistent Investment in R&D for Technological AdvancementPrivate Sector InvestmentThe investment budget of private companies in the aerospace sector continued increasing until 2020, before the pandemic hit Korea and cut investment by 17% year-on-year in 2021. However, the investment amount reached higher than pre-pandemic level from 2022. As of 2022, the private sector of the aviation industry has focused on investing in technology development and facility/equipment.
* Of total investment budget, 61% goes to R&D, while 25% goes to facility/equipment.
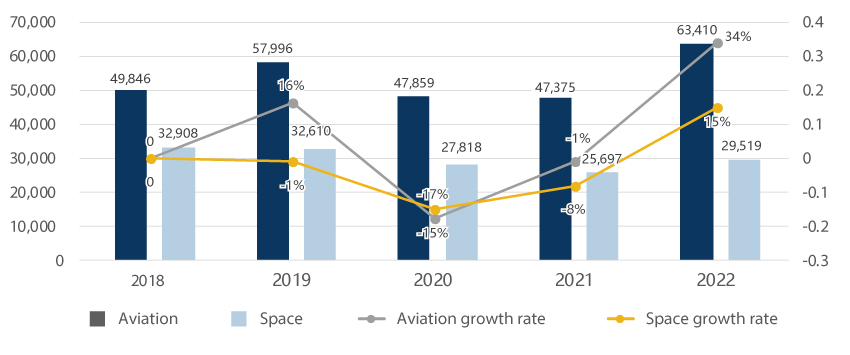
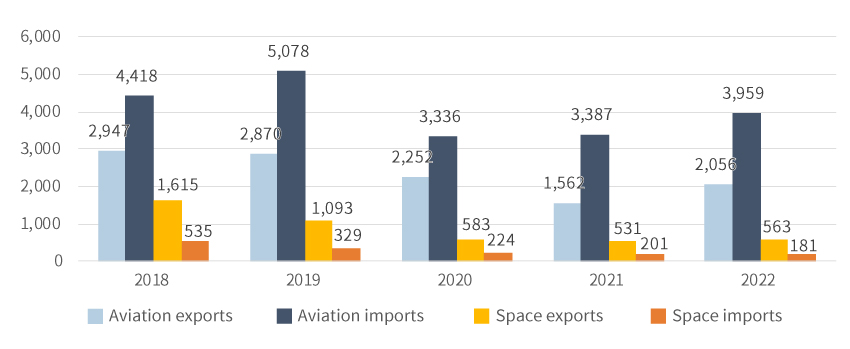
As of 2022, private companies in the aerospace industry invested 55% of total investment budget in R&D. Compared to the previous year, the share of R&D out of total investment budget declined about 18%, while that of facility/equipment increased 18%."Investment by Private Companies in the Aerospace Industry"(unit: KRW 1 million)(unit: KRW 1 million)민간기업의 항공 및 우주산업 투자 현황으로 구분, 연도별 정보제공 Category 2019 2020 2021 2022 Aviation R&D 184,875 270,865 258,899 322,935 Facility/Equipment 179,876 178,809 130,949 130,282 Land/Building 137,750 142,045 47,393 58,506 Others 28,698 27,317 21,481 19,099 Subtotal 531,017 619,036 458,723 530,822 Space R&D 151,576 134,784 150,522 168,084 Facility/Equipment 27,422 80,219 54,634 138,871 Education Training 1,046 2,486 670 1,256 Others - - - - Subtotal 180,065 217,489 205,826 308,211 Total 711,082 836,525 664,549 839,033 ※ Source: Korea Aerospace Industries Association (Industry DB), Survey on the Aerospace Industry (2023)Private Sector SalesThe aviation industry continued growth until 2019, but it was seriously affected by COVID-19 to see sales plunge by 13% in 2020 and the decline continued throughout 2021. However, the sales recovered to the pre-COVID-19 level in 2022. When it comes to the space industry, the sales continued to decline by 2021. However, the sales began recording a growth momentum in 2022 with the arrival of the era of New Space."Private Sector Sales (2018-2022)"(Unit: KRW 100 million)(Unit: KRW 100 million)민간분야 매출액 현황 (’18 ~’22) 정보제공 Category 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Aviation Sales 49,846 57,996 47,859 47,375 63,410 Growth Rate - 16% -17% -1% 34% Space Sales 32,908 32,610 27,818 25,697 29,519 Growth Rate - -1% -15% -8% 15% ※ Source: Korea Aerospace Industries Association (Industry DB), Survey on the Aerospace Industry (2023)Private Sector Imports and ExportsAs the aviation industry is characteristically dependent on imports, for its materials and parts, its trade balance typically remains deficit. When it comes to the space industry, the export volume has continued to decline until 2021, but slightly grown since 2022, while the trade balance has continued to record surplus."Private Sector Imports and Exports (2018 - 2022)"(unit: USD 1 million)(unit: USD 1 million)수출입 현황 (’18~’22) 정보제공 Category 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Aviation Exports 2,947 2,870 2,252 1,562 2,056 Imports 4,418 5,078 3,336 3,387 3,959 Trade Balance -1,471 -2,208 -1,083 -1,825 -1,903 Space Exports 1,615 1,093 583 531 563 Imports 535 329 224 201 181 Trade Balance 1,080 764 359 330 382 ※ Source: Korea Aerospace Industries Association (Industry DB), Survey on Space Industry (2023)
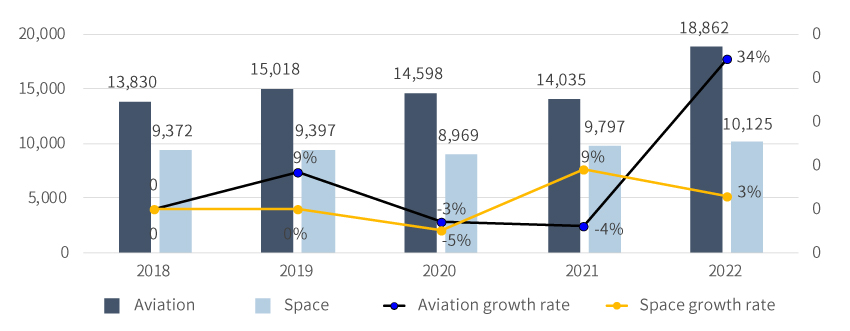
※ Exchange rate applied: Woori Bank’s annual average exchange rate for each year (first announced)Private Sector EmploymentThe number of aviation personnel was 17,638 in 2021, and the industry maintained the level since 2017 with minor changes. Employment in the space industry reached 7,317 in 2021, demonstrating a temporary decline due to the pandemic in 2020 before increasing by 16% year-on-year driven by rising interest in the space sector."Private Sector Employment (2018 - 2022)"(unit: Persons)(Unit: Persons)민간분야 고용 현황 (’18 ~’22) 정보제공 Category 2018 2019 2020 2021 2017 Aviation No. of employees 13,830 15,018 14,598 14,035 18,862 Growth rate - 9% -3% -4% 34% Space No. of employees 9,372 9,397 8,969 9,797 10,125 Growth rate - 0% -5% 9% 3% ※ Source: Korea Aerospace Industries Association (Industry DB), Survey on Space Industry (2023)Major achievements in R&D-
(Space) Successful Launch of Korea’s First Mass-Produced Nanosatellite (Launched on April 24, 2024)
- Korea’s First Mass-Produced Nanosatellite, scheduled for periodic imaging of the Korean Peninsula and areas of interest from approximately 500km above Earth to commence from November 2024, has been confirmed for normal operation and communication. It is the Earth Observation Satellite, developed by KAIST since 2020 under the Nanosatellite Constellation System Development Project with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSTI) and the National Intelligence Service. This successful launch will support the economic feasibility of commercial products, in the time of the private-led era, and lay the foundation to actively support space-related industries.
-
(SPACE) Laid the foundation for Korea’s own space exploration with the successful development and launch of Danuri (Korean Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter) (Dec 2022)
- The successful launch serves as a stepping stone for future lunar landers and space exploration and for scientific missions as Danuri is collecting scientific data in six payloads.
-
(SPACE) Successful development and launch of Nuri provides Korea with space transportation capability
- Korea laid the foundation for revitalizing the space industry and building the infrastructure for producing space launch vehicles, including engine technology and systems, and test facilities. Transfer of Nuri’s technologies to businesses also contributed to building the ecosystem of the space industry.
-
(SPACE) Successful development and launch of the next-generation mid-sized satellite No.1 (Mar. 2021)
- Korea developed its own 500kg-class satellite technologies and domestically developed key components of the optical payload. Korea can now provide satellite data to meet various needs including land and resources management and disaster response. Transfer of satellite development technologies to businesses and improved capabilities of space companies laid the foundation to revitalize the satellite industry.
-
(Aviation) South Korea selects Embraer’s C-390 for the Air Force’s new large transport aircraft (December 2023)
- Embraer was finally selected based on its high score for the collaboration consortium with domestic companies. It is expected to work in connection with the development of Korea’s MC-X (Multi-role Cargo).
-
(Aviation) South Korea-Poland, Sign Mutual Military Airworthiness Certification (January 2024))
- South Korea’s Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), based on close defense cooperation, has signed a deal with Poland to establish a mutual recognition process for military airworthiness certification, a key measure of a plane’s suitability for safe flight. Under the mutual recognition process, Warsaw will recognize Seoul’s airworthiness certification for South Korean-made planes and vice versa.
-
(Aviation) Development of “Inconel718 superalloy casting and forging for turbofan engine launched (July 2023)
- As part of technology development project of the Ministry of Industry, Trade, and Energy, Hanwha Aerospace held a project launching meeting and MOU signing ceremony to develop “Inconel718 superalloy casting and forging for turbofan engine” with the Korean Aerospace Technology Research Association, the Korea Planning & Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and Seoul National University. It is expected to solidify the self-reliant national defense capability and aerospace GVC through localization of engine parts in the future.
-
Entry into the UAM Market
- With the UAM market expected to enjoy an exponential growth, Hyundai Motor Group’s entry into the market raised expectations of active participation of related Korean businesses in the aviation industry and the resulting ripple effect.
-
(Space) Successful Launch of Korea’s First Mass-Produced Nanosatellite (Launched on April 24, 2024)
-
Global Companies Open R&D Ceners and Production Base in Korea 내용열기Here and Now Global Companies Open R&D Centers and Production Base in KoreaUS-based Boeing established the world’s largest Boeing Korea Engineering and Technology Research Center (BKETC) in Seoul in 2019 and is creating synergies by collaborating with Korean communication, semiconductor and manufacturing sectors. The BKETC has recruited and hired experts in autonomous flight, artificial intelligence, avionics, mobility platforms, smart cabins, and smart factories to study next-generation aerospace technologies."Next-Generation Cutting-edge Aerospace Technologies: Research Areas"
-
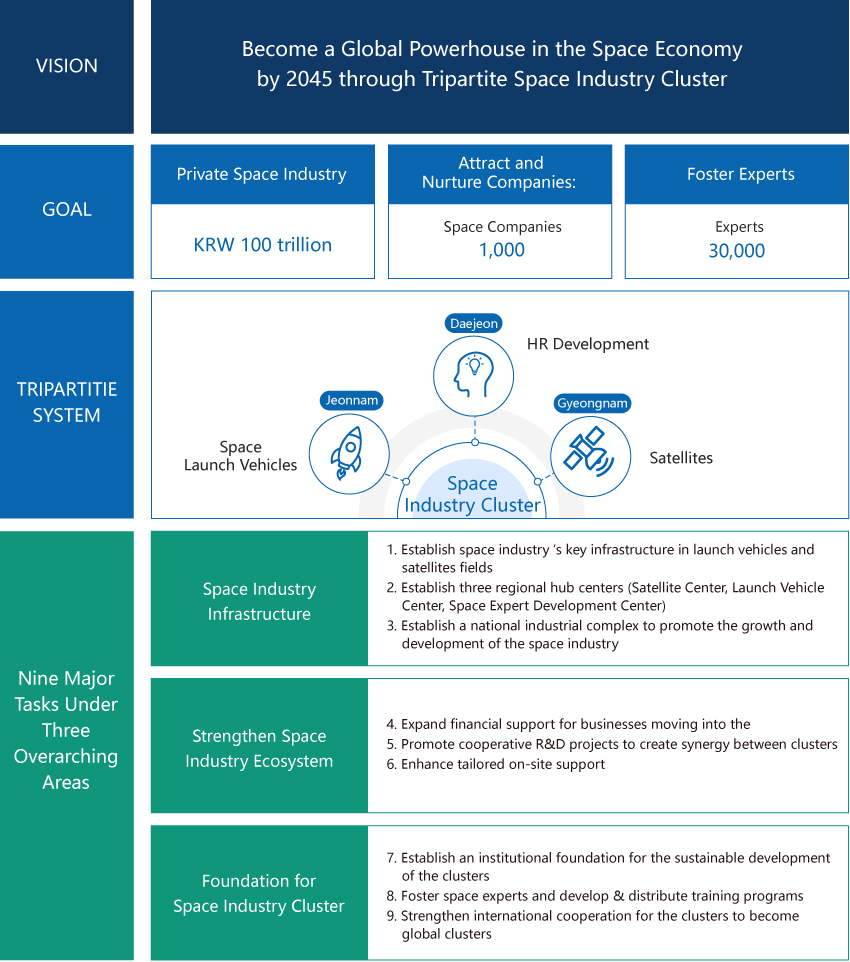
Towards a Global Aerospace Powerhouse 내용열기Towards a Global Aerospace PowerhouseEstablishment of the Korea AeroSpace Administration (KASA)With the passage of the special bill on the establishment of the Korea AeroSpace Administration through the National Assembly, the process for the establishment of the space agency was launched in full scale. With the Future space Economy Roadman in 2022 as a start, the Preparatory Office for the Korea Space and Aeronautics Administration was launched as the preparation for the establishment of an aerospace agency. It led to the government submitted the legislative bill to the National Assembly in April 2023. The bill passed the National Assembly on January 9, 2024, making the establishment of an independent aerospace organization a final.KASA is set to foster aerospace companies, create jobs in the aerospace industry, and expand the government’s investment in the aerospace industry. It has been planned to provide active support so that the aerospace industry can be a future growth engine of Korea.KASA is scheduled for opening its office in May 2024 in Sacheon-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, a hub of the aerospace industry and home to the National Aerospace Industrial Complex.Aerospace designated as one of the 12 national strategic technologiesThe government has designated aerospace as one of the 12 national strategic technologies, emphasizing its strategic importance at the national level and actively supporting it for future growth and independent development of technologies. The aerospace and marine category encompasses large multi-stage combustion cycle engines, space observation and sensing, lunar landing and surface exploration, and high-tech aviation gas turbine engines and components. To promote urban air traffic (UAM) categorized as high-tech mobility, the government has put together a draft of the Enforcement Decree of the Special Act on Fostering National Strategic Technologies, which will soon be enacted. Moreover, the Korean government announced the Future Space Economy Roadmap (in Nov. 2022), presenting policy directions to grow as an aerospace powerhouse. It also announced the Fourth Master Plan for Space Development Promotion (in Dec. 2022) to set the country's mid- and long-term objectives and directions for space development.Moreover, the Korean government announced the Future Space Economy Roadmap (in Nov. 2022), presenting policy directions to grow as an aerospace powerhouse. It also announced the Fourth Master Plan for Space Development Promotion (in Dec. 2022) to set the country's mid- and long-term objectives and directions for space development. In addition, the government, based on the Korean Urban Air Traffic (K-UAM) Roadmap, is promoting policies aimed at commercializing UAM, the next-generation mobility urban air traffic, by 2025. To that end, the government is supporting private-led projects, establishing a new framework system, different from the existing one overseeing safety and transportation, and encouraging businesses to enter and grow in the high-tech area by applying global standards. Moreover, the government, in consideration of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is promoting R&D policies to stay competitive in future key areas. By focusing on developing Korea's own aviation engine technologies, three major avionics technologies (sensors, flight control, and navigation) and ICT convergence technologies, the government aims to strengthen capabilities to participate in international joint development projects and targeting ICT convergent niche markets such as UAV and smart cabins."Fourth Master Plan for Space Development Promotion: Vision and Strategy"

VISON
Leader of the Global Space Economy by 2045
Targets
Expand the scale of space exploration
- Fulfill key space exploration missions
- (Currently in 2022) Lunar orbiter mission
- (2032) Lunar landing and surface exploration
- (2045) Mars landing
Increase investment in space development
- Govt’s investment in aerospace development
- (‘Currently in 2021) KRW 0.73 trillion
- (2027) KRW 1.5 trillion (double)
Generate private aerospace industry
- Share in the global aerospace industry market (based on sales)
- (Currently in 2021) About 1%
- (2045) 10% (equivalent to other major industries)
Announcement of five missions as long-term strategic goals and two strategies as means of implementation
Five main long-term missions for space development
Expand investment in space development
- 01. Expand space exploration: Execute Korea’s own space exploration plans
- 02. Fulfill space transportation: Complete the service capability and infrastructure for space transportation
- 03. Generate the space industry: Develop the space industry into main industry
- 04. Promote space security: Build the system for supporting space and ground security
- 05. Promote space science: pioneering research led by Korean scientists
Strategies
Strategy 1: Lay the foundation for space economy
- Industrial ecosystem
- Governance
- Procuring specialists
- Global leadership
- Space security system
Strategy 2 : Develop cutting-edge space technologies
- Launch vehicles and infrastructure
- Satellites and services
- Space exploration·Science
 ※ Source: Fourth Master Plan for Space Development Promotion for implementation of the Future Space Economy Roadmap (2022)Three-Axis System of Space Industry ClustersThe government designated Jeonnam (launch vehicle), Gyeongnam (satellite), and Daejeon (research and talent development) as space industry clusters to foster the space industry led by the private sector.
※ Source: Fourth Master Plan for Space Development Promotion for implementation of the Future Space Economy Roadmap (2022)Three-Axis System of Space Industry ClustersThe government designated Jeonnam (launch vehicle), Gyeongnam (satellite), and Daejeon (research and talent development) as space industry clusters to foster the space industry led by the private sector.
(Definition) An area developed by interconnecting research institutes, enterprises, educational institutions, and science and technology related institutions and organizations with the relevant support facilities to facilitate the convergence and integration of the space industry and the development in connection with related industries < br/> (Structure) Designate and foster Jeonnam (Goheung), Gyeongnam (Jinju, Sacheon), Daejeon (Yuseong) as a cluster for launch vehicle, satellite, and R&D and training experts, respectively (Tripartite Space Industry Cluster)
(Ground) Policy Task (No. 79, Emerge as Space Powerhouse and Open Korea’s Space Era), the “Space Economy Roadmap (November 202, the “Fourth Basic Plan for Promoting Space Development (December 2022)”"Space Industry Cluster Three-Axis System"Carry out the establishment of core infrastructure and hub as planned, advancing capabilities of each special zone1. Special zone for launch-vehicles: Create the industrial ecosystem centered by Naro Space Center → Emerge as “Asia’s leading space port”
2. Special zone for satellites: Integrate development and manufacturing foundations in connection with the establishment of KASA
3. Special zone for R&T professionals: Generate synergy effect by brining together research and expert training capabilities of the industry-academia-researchLarge-scale financial investment and institutional improvement to attract corporates’ investment and facilitate private investment1. Financial investment: Intense investment of more than KRW 1 trillion in total by 2031
2. Institutional improvementSelect 9 major tasks under 3 overarching areas to swiftly promote and generate innovation and achievements- Space Industry Infrastructure
- Establish space industry ‘s key infrastructure in launch vehicles and satellites fields
- Private Rocket Launch Site
- satellite testing infrastructure
- Establish three regional hub centers to concentrate the clusters’ capabilities
- Satellite Center, Launch Vehicle Center, Space Expert Development Center
- Establish a national industrial complex to promote the growth and development of the space industry
- Establish space industry ‘s key infrastructure in launch vehicles and satellites fields
- Strengthen Space Industry Ecosystem
- Expand financial support for businesses moving into the clusters
- Scale-up the space fund up to more than KRW 100 billion by 2027, and focused investment in promising tenant companies in the clusters
- Promote cooperative R&D projects to create synergy between clusters
- Regional cooperative satellite projects, etc.
- Enhance tailored on-site support to crate the foundation for space industry ecosystem
- Support materials, parts, and equipment R&D in the space field (satellite testing and launch environment), Establish a support system
- Expand financial support for businesses moving into the clusters
- Foundation for Space Industry Cluster
- Establish an institutional foundation for the sustainable development of the clusters
- Special Act Legislation, Development Committee, Deregulation
- Foster space experts and develop & distribute training programs
- Establish a national talent training platform
- Talent training based on R&D
- Strengthen international cooperation for the clusters to become global clusters
- Establish a global cooperation system, facilitate an international exchange
- Establish an institutional foundation for the sustainable development of the clusters
Companies in the space industry are mainly concentrated in the Seoul Metropolitan Area and Chungcheong Province (375, 73.6%). In the Seoul Metropolitan Area, various space-related companies (264) are operating, including satellite and launch vehicle manufacturers, while major satellite-related companies such as Satrec Initiative are based in Chungcheong Province." Key Players and Infrastructure in the Aviation Industry by Region "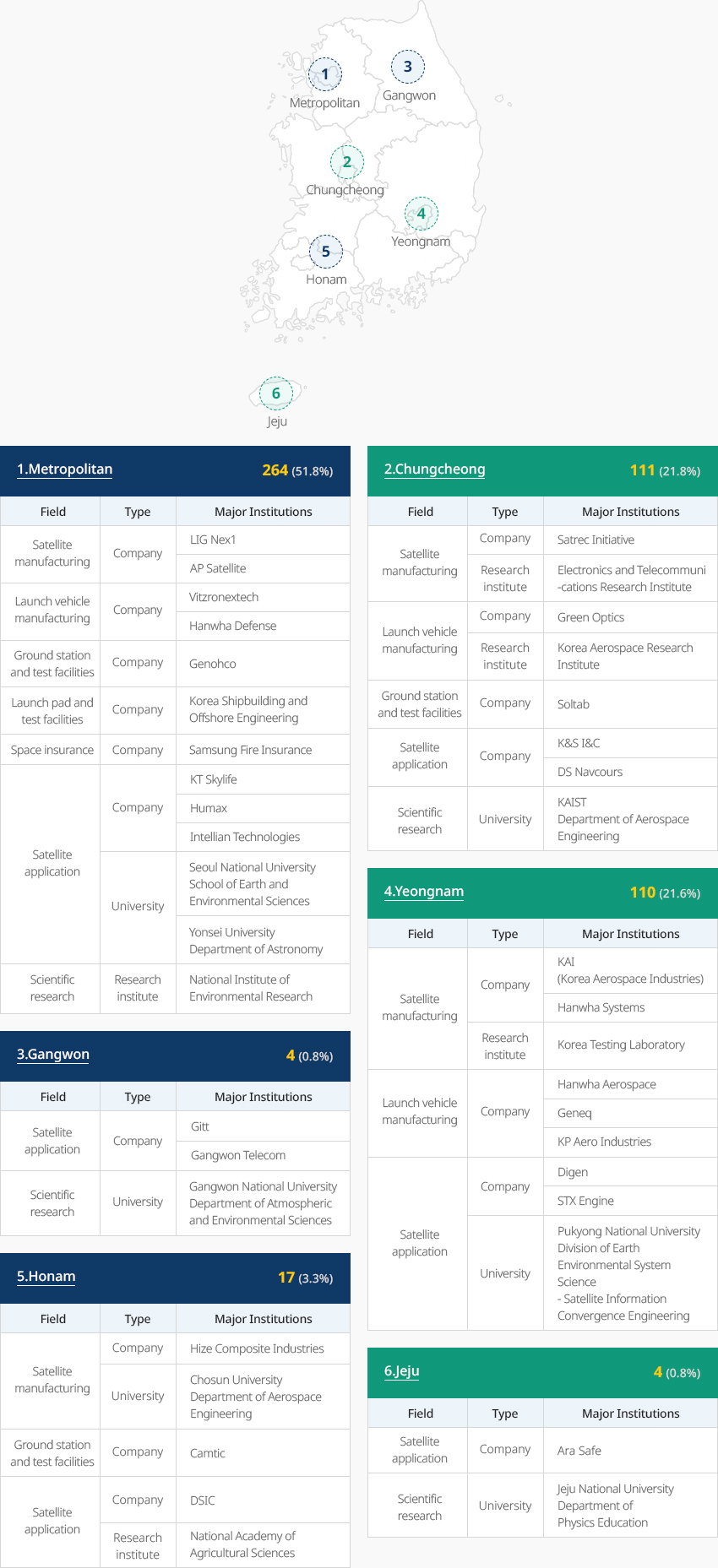
-
수도권 227개(50.6%)
우주산업 지역별 주요 기업 및 인프라(수도권) 표로 분야, 구분, 주요 기업 정보제공 분야 구분 주요 기업 우주 기기 제작 기업체 (주)엘아이지넥스원 에이피 위성(주) 연구 기관 국립환경과학원 대학 서울대학교 기계항공공학부 우주항공공학전공 위성 활용 기업체 (주)휴맥스 (주)케이티스카이라이프 케이티샛 대학 아주대학교 우주전자정보공학과 경희대학교 국제캠퍼스 우주과학과 연세대학교 천문우주학과 -
강원권 6개(1.3%)
우주산업 지역별 주요 기업 및 인프라(강원권) 표로 분야, 구분, 주요 기업 정보제공 분야 구분 주요 기업 위성활용 기업체 지트 우주활용 대학 상지대학교 건설시스템공학과 강릉원주대학교 대기환경과학과 -
충청권 114개(25.4%)
우주산업 지역별 주요 기업 및 인프라(충청권) 표로 분야, 구분, 주요 기업 정보제공 분야 구분 주요 기업 우주기기 제작 기업체 (주)쎄트렉아이 한국항공우주연구원 연구기관 한국기초과학 지원연구소 대학 한국과학기술원 항공우주공학과 우주활용 기업체 넴코어스 (주)케이앤에스 아이앤씨 연구기관 기상청 국가기상위성센터 한국천문연구원 대학 한국과학기술원 항공우주공학과 충남대학교 천문우주과학과 -
영남권 85개(18.9%)
우주산업 지역별 주요 기업 및 인프라(영남권) 표로 분야, 구분, 주요 기업 정보제공 우주기기 제작 기업체 한화에어로스페이스 한국한공우주산업(주) 연구기관 한국해양과학기술원 위성활용 기업체 (주)디젠 대학 울산과학기술원 도시환경공학부 환경과학공학전공 -
호남권 14개(3.1%)
우주산업 지역별 주요 기업 및 인프라(호남권) 표로 분야, 구분, 주요 기업 정보제공 분야 구분 주요 기업 우주기기제작 기업체 데크항공(주) 캠틱종합기술원 우주활용 연구기관 국립농업과학원 대학 전북대학교 항공우주공학과 -
제주권 2개(0.6%)
우주산업 지역별 주요 기업 및 인프라(제주권) 표로 분야, 구분, 주요 기업 정보제공 분야 구분 주요 기업 위성활용 기업체 아라세이프 우주활용 연구기관 국립전파연구원 우주전파센터
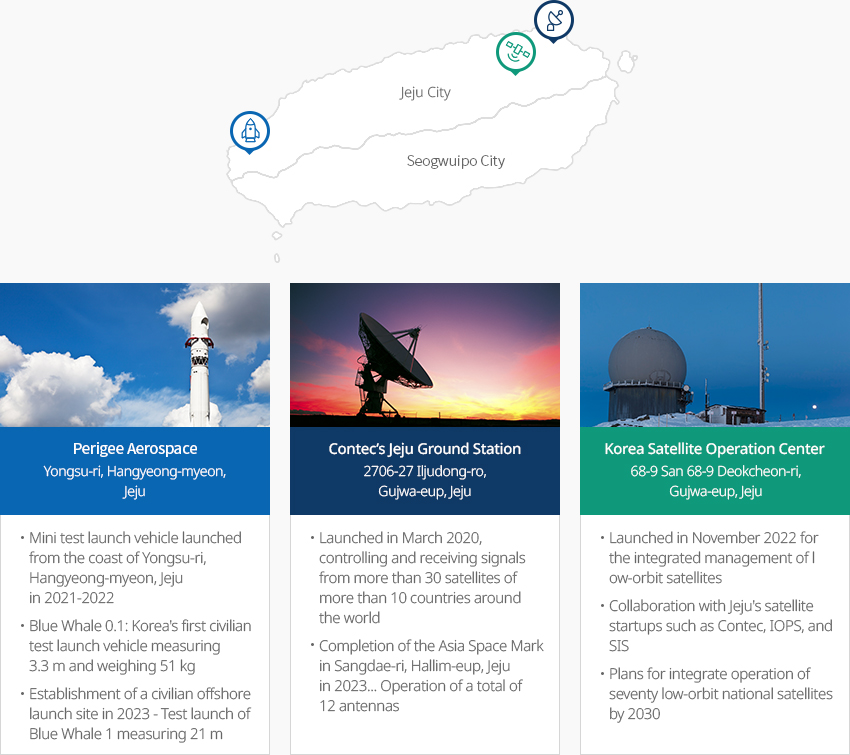
 ※ Source: Survey on the Aerospace Industry (2022)The Jeju Provincial Government is striving to transform Jeju into an outpost of the New Space Age by opening the Korea Satellite Operations Center, building an offshore launch site for space launch vehicles, and signing business agreements with private space companies. Contec, IOPS, SIIS, and Perigee Aerospace have built their bases in Jeju by signing agreements with the Jeju Provincial Government." Key Players and Infrastructure in the Space Industry by Region "※ What's Happening in Jeju? Space Startups Rush to Jeju looking for a Radio-Free Zone, Money Today article on May 18, 2023
※ Source: Survey on the Aerospace Industry (2022)The Jeju Provincial Government is striving to transform Jeju into an outpost of the New Space Age by opening the Korea Satellite Operations Center, building an offshore launch site for space launch vehicles, and signing business agreements with private space companies. Contec, IOPS, SIIS, and Perigee Aerospace have built their bases in Jeju by signing agreements with the Jeju Provincial Government." Key Players and Infrastructure in the Space Industry by Region "※ What's Happening in Jeju? Space Startups Rush to Jeju looking for a Radio-Free Zone, Money Today article on May 18, 2023
-
Complex nameSacheon 1st General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date1991.12.28
-
Designated area(m2)2,545,259
-
ManagementGyeongsangnam-do Sacheon City, Korea Industrial Complex Corporation
-
Nearby RailwayJinju Station
-
Distance from station(km)14
-
Nearby AirportSacheon Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)5
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)11000(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentGyeongsangnam-do Sacheon City
-
Population111,440
-
Complex nameGokyong General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2009.12.24
-
Designated area(m2)1,565,077
-
ManagementGyeongsangbuk-do Yeongcheon City
-
Nearby RailwayYeongcheon Station
-
Distance from station(km)10
-
Nearby AirportDaegu International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)52
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)2053(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentGyeongsangbuk-do Yeongcheon City
-
Population101,523
-
Complex nameJeonggwan Agricultural Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date1987.02.25
-
Designated area(m2)258,083
-
ManagementBusan Metropolitan City Gijang County
-
Nearby RailwayBusan Station
-
Distance from station(km)31
-
Nearby AirportGimhae International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)35
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)400(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentBusan Metropolitan City Gijang County
-
Population172,288
-
Complex nameSapo General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2004.12.16
-
Designated area(m2)745,994
-
ManagementGyeongsangnam-do Miryang City
-
Nearby RailwayMiryang Station
-
Distance from station(km)4
-
Nearby AirportGimhae International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)51
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)1996(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentGyeongsangnam-do Miryang City
-
Population105,026
-
Complex nameMadong Agricultural Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2007.08.06
-
Designated area(m2)287,799
-
ManagementGyeongsangnam-do Goseong County
-
Nearby RailwayMasan Station
-
Distance from station(km)47
-
Nearby AirportSacheon Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)38
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)-
-
Affiliation local governmentGyeongsangnam-do Goseong County
-
Population26,867
-
Complex nameDuryang Specialized Agricultural Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2004.06.10
-
Designated area(m2)118,161
-
ManagementGyeongsangnam-do Sacheon City
-
Nearby RailwayJinju Station
-
Distance from station(km)9
-
Nearby AirportSacheon Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)5
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)-
-
Affiliation local governmentGyeongsangnam-do Sacheon City
-
Population111,401